Abstract
Background: The incorporation of modern day induction regimens, autotransplant and continuous maintenance has resulted in better long-term outcomes for myeloma patients. Experience and trials demonstrated that by prolonging 1st progression-free survival (PFS1) and pushing the relapse farther, we can gain the OS advantage (McCarthy et al NEJM 2012). Unfortunately, a subgroup of patients fail to exploit this advantage, either due to their disease biology or due to inadequate therapy and suffer early progression (inferior PFS1) that impacts their long term outcomes. First, we evaluated the predictors of early progression to highlight the modifiable factors that can prevent progression. Next, we quantified the impact of shorter PFS1 (<36 months) on the long-term survival (OS).
Methods: Of the 1000 consecutive newly diagnosed myeloma patients treated with homogenous induction therapy (RVD) induction therapy per Richardson et al (Blood 2010) from July 2005 until August 2016, 230 patients progressed within the first 36 months while 96 patients progressed beyond the 36-month mark, at the time of analysis. Median follow up duration was 38 months. Demographic and outcomes data for the pts were collected from myeloma database and responses were evaluated per IMWG Uniform Response Criteria.
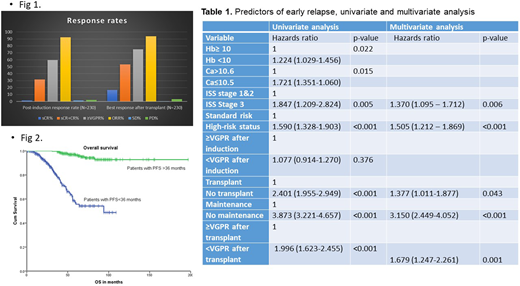
Results: Median age of the pts is 60 years (range 29-78). 29% of the patients are above the age of 66. M/F 54%/46%; W/AA 60%/32%; ISS III 27% were other patient characteristics. Cytogenetic abnormalities of significance: t(11;14): 13.5%, t(4;14): 7.8%, t(14;16): 5% del 17p: 16%, complex cytogenetics: 29% and high-risk status was conferred to 44% of the patients. 83% of patients underwent an autotransplant and median time to transplant was 6 (2-50) months. 68% of patients received maintenance therapy. Response rates are summarized in Fig 1. The median PFS for early and non-early progressors were 32 months (95% confidence interval (CI), 30.293-33.707) and 101 months (95% CI, 77.14-124.86) months, respectively (P<0.001). The median overall survival (OS) for early progressors was 94 months, and non-early progressors was not reached. (Fig 2). Among the predictors of early relapse, presence of high-risk status, ISS stage 3, inability to achieve ≥VGPR after transplant, non-receipt of transplant and/or maintenance were independent predictors of early progression on the multivariate analysis as illustrated in Table 1.
Conclusions: Even with the effective use of the 3-drug induction regimen, these functionally high-risk patients that are early progressors have truncated long term survival. Our analysis advocates for using transplant, deepening the responses with modern drugs such as monoclonal antibodies to achieve ≥VGPR after transplant and intense maintenance strategies to prevent relapse.
Nooka:Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Adaptive technologies: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kaufman:Abbvie: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Other: data monitoring committee; Roche: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy. Hofmeister:Adaptive biotechnologies: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Boise:AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy. Heffner:ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. Lonial:Amgen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.